For several years now, Model-Based Testing is mainly used within the (technical) development processes. In the Black Box testing community it was still "just a theory", and in my case: fun to play with. Today is different! I'm completely into Model-Based Testing nowadays. MBT turned, for Black Box testers, into serious business!
For quite some years I'm working with a tool called COVER. Initially COVER was build to help lazy testers, like me, to avoid boring manual activities…and it worked! Using this tool I could easily amaze my surrounding with stunning Speed and Quality. Especially deriving test cases from formal specifications like pseudo code or activity diagrams was fun to do; instead of "solving a boring puzzle" time, it was done in seconds (as a matter of speaking). However, most of the testers in my surrounding didn't recognize the ease of this way of working (or were not lazy enough?) so COVER didn't have much users.
Today is different. The attention for Model-Based Testing is growing rapidly. Previously, when a project had to make test cases, it was accepted that it was done manually and, everybody knew, it should take quite some time.
Today the budgets are lowered...What to do?...Less productivity?
My suggestion: When you've less money to spent, be creative to get the same results!
First Model then Test!
Model-Based Testing is a nice example of creative thinking!
Within a few months the relatively unknown possibilities of Model-Based Testing tools became very popular for Black Box testers within Sogeti. Especially the collaboration-part (designers working together with testers) of Model-Based testing is an eye opener. Everybody knows that it is smart to find defects as early as possible, but it is very difficult to motivate teams to perform good design inspections. Now MBT tools like COVER can do a big part of those intensive inspections, because using the models for generating test cases will directly show the defects in those models in a very early phase of the project! And beside that, it generates a big part of the test cases!
So, when the Designers create models that COVER understands, projects will perform Better, Faster and Cheaper! ....and it works!
Some (early) successes from our proof-of-concepts and implementations:
Collaboration will change the world of testers!
Using MBT is in fact collaborating within the Application Lifecycle [ALM] supported by standardization and automation. Many defects, found in functional testing, have their origin in misinterpretations and assumptions of the requirements and/or specifications. The early usage (generating test cases) of formal models, just after or during the design phase, will create a much more solid base for software coding. For the testers this will mean less and less defects, so besides the generated test cases, the improved quality of the software will also fasten the test process.
(PS. When both software and test cases are generated from the same models, be sure that the test objective is clear!)
This industrialization can’t be stopped anymore. The time of creating most test cases by hand has had its peak. Of course, not all test cases can be generated, and also manual testing itself will never disappear, but handcrafted test cases will be less and less common practice. The work of Black Box testers will, in my opinion, shift in two directions: 1) Earlier in the life cycle: joined modeling and helping and supporting development to find defects as early as possible (Master Test Plan consultancy), or 2) the coming market End-to-End testing: the importance of complete chains of applications is growing rapidly. End-to-End Testing will become a separate specialism.
Examples
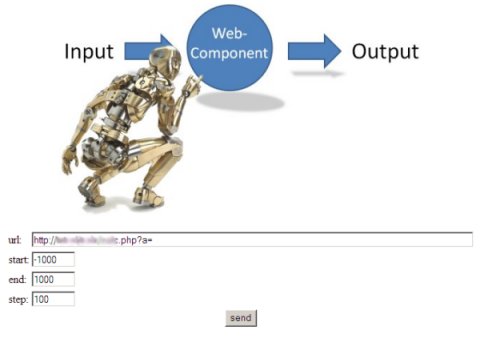
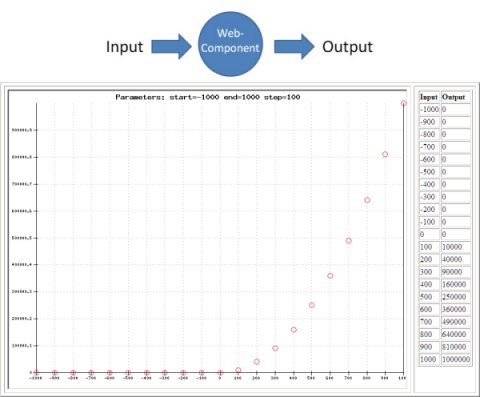
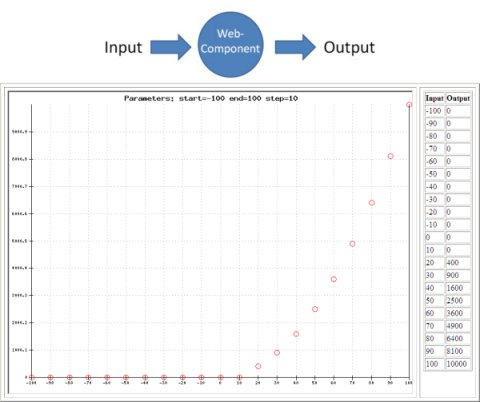
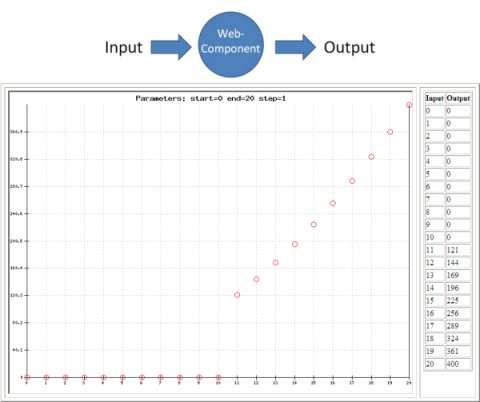
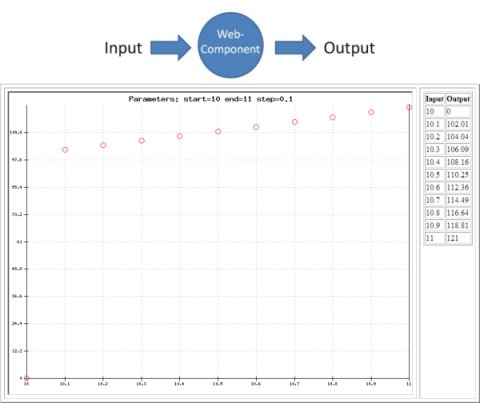
Back to Model-Based Testing: To give an idea what type of models can be used, and how test cases are generated, I've made a some slides (with examples) about the Sogeti MBT tool: COVER. Look for yourself if MBT will affect your work!
It did affect mine!

Rob Kuijt
Wikipedia:
Model-Based Testing is software testing in which test cases are derived in whole or in part from a model that describes some (usually functional) aspects of the system under test (SUT).
 |
For quite some years I'm working with a tool called COVER. Initially COVER was build to help lazy testers, like me, to avoid boring manual activities…and it worked! Using this tool I could easily amaze my surrounding with stunning Speed and Quality. Especially deriving test cases from formal specifications like pseudo code or activity diagrams was fun to do; instead of "solving a boring puzzle" time, it was done in seconds (as a matter of speaking). However, most of the testers in my surrounding didn't recognize the ease of this way of working (or were not lazy enough?) so COVER didn't have much users.

Today is different. The attention for Model-Based Testing is growing rapidly. Previously, when a project had to make test cases, it was accepted that it was done manually and, everybody knew, it should take quite some time.
Today the budgets are lowered...What to do?...Less productivity?
My suggestion: When you've less money to spent, be creative to get the same results!
Model-Based Testing is a nice example of creative thinking!
Within a few months the relatively unknown possibilities of Model-Based Testing tools became very popular for Black Box testers within Sogeti. Especially the collaboration-part (designers working together with testers) of Model-Based testing is an eye opener. Everybody knows that it is smart to find defects as early as possible, but it is very difficult to motivate teams to perform good design inspections. Now MBT tools like COVER can do a big part of those intensive inspections, because using the models for generating test cases will directly show the defects in those models in a very early phase of the project! And beside that, it generates a big part of the test cases!
So, when the Designers create models that COVER understands, projects will perform Better, Faster and Cheaper! ....and it works!
Some (early) successes from our proof-of-concepts and implementations:
- The amount of time needed for creating test cases dropped 50% (and sometimes more);
- The maintenance of the (regression) test cases became in average 70-80% cheaper;
- And maybe most important: We have proved to find defects much earlier than the project did manually!
Collaboration will change the world of testers!
Using MBT is in fact collaborating within the Application Lifecycle [ALM] supported by standardization and automation. Many defects, found in functional testing, have their origin in misinterpretations and assumptions of the requirements and/or specifications. The early usage (generating test cases) of formal models, just after or during the design phase, will create a much more solid base for software coding. For the testers this will mean less and less defects, so besides the generated test cases, the improved quality of the software will also fasten the test process.
(PS. When both software and test cases are generated from the same models, be sure that the test objective is clear!)
This industrialization can’t be stopped anymore. The time of creating most test cases by hand has had its peak. Of course, not all test cases can be generated, and also manual testing itself will never disappear, but handcrafted test cases will be less and less common practice. The work of Black Box testers will, in my opinion, shift in two directions: 1) Earlier in the life cycle: joined modeling and helping and supporting development to find defects as early as possible (Master Test Plan consultancy), or 2) the coming market End-to-End testing: the importance of complete chains of applications is growing rapidly. End-to-End Testing will become a separate specialism.
Examples
Back to Model-Based Testing: To give an idea what type of models can be used, and how test cases are generated, I've made a some slides (with examples) about the Sogeti MBT tool: COVER. Look for yourself if MBT will affect your work!
It did affect mine!
Rob Kuijt




 ( 3 / 2165 )
( 3 / 2165 )





 Calendar
Calendar





