We, professional testers, are proud that we can create good test cases from bad requirements.....That's a great achievement.......We can save projects much time by starting with the test process at an early stage in the life cycle........Or not? Who are we doing a favor?
Believe it or not, with test specification techniques like 'Data Combination Test' it is possible to create good test cases from incomplete and/or vague requirements. By combining the (bad) requirements with the knowledge of domain specialists in creative team sessions, it is possible to create great test cases, with even the choice to cover the risks with different test depths levels.
So, if the requirements team runs out of time (or don't understand their own job properly);
No problem;
Send the stuff;
We can start right away with the preparation of the test cases.
It is fun to do, it saves time and we do find many defects with this approach!
GREAT job! or NOT? ............Is deriving good test cases from bad requirements professionalism?
Let's look at the Project level
Besides us testers there are more parties trying to do their jobs on base of the requirements. For instance can the development team build the software? ....Yes, they can! Most teams are very experienced in making assumptions and interpretations, so bad requirements are not a problem.
OK, and the project managers? Can they do their job? Yes, they can...not an easy job, and sometimes a project don't make it or has some delays, but what the hack, that's how it works in the ICT!
GREAT job! or NOT?............What about the customers? Do we solve their problems?
Let's look at the Application Lifecycle Management [ALM] level
Try to answer this question: If the same bad requirements are sent to 10 different projects with the same assignment to make the needed Information System. What is the change that the projects will deliver an Information System that solves the problems of the customer?..............I think that, of course depending on the amount of communication with the customer during the projects, the changes are not very great, maybe some projects will, but most of them will need more than one release....
And that's NOT a GREAT job!
I know....we testers can't solve this problem.... but what, if we stop accepting Verbal Diarrhea as a test base....
What will happen if testers refuse to make test cases from bad requirements?

Or even....what happens if testers create, as a first step of the activity 'test case specification', for instance during the testability review, formal models like process flows or activity diagrams?
Problems like interpretations and/or assumptions rise instantly, and if these problems in the requirements can be solved before the development team start building the software, it would differ a lot!!
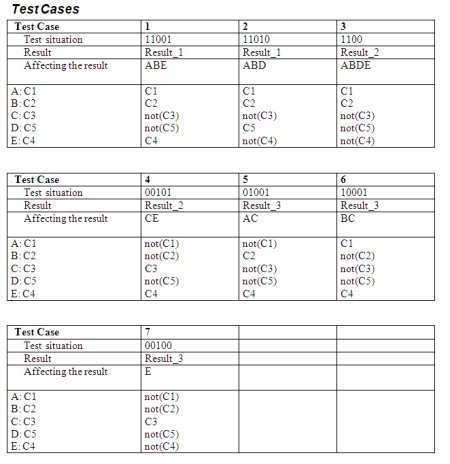
In this 'First Model then Test'(FMTT) approach , we can use the following set of models:
Disadvantages of FMTT:
Advantages of 'First Model then Test' (FMTT):
Afraid to be bored by less complexity?
Try to make the next step: Model Based Development, Testing and/or Estimation!
I've already proved that generating test cases from models is possible (see previous articles on that subject).
Rob Kuijt
Believe it or not, with test specification techniques like 'Data Combination Test' it is possible to create good test cases from incomplete and/or vague requirements. By combining the (bad) requirements with the knowledge of domain specialists in creative team sessions, it is possible to create great test cases, with even the choice to cover the risks with different test depths levels.
So, if the requirements team runs out of time (or don't understand their own job properly);
No problem;
Send the stuff;
We can start right away with the preparation of the test cases.
It is fun to do, it saves time and we do find many defects with this approach!
GREAT job! or NOT? ............Is deriving good test cases from bad requirements professionalism?
Let's look at the Project level
Besides us testers there are more parties trying to do their jobs on base of the requirements. For instance can the development team build the software? ....Yes, they can! Most teams are very experienced in making assumptions and interpretations, so bad requirements are not a problem.
OK, and the project managers? Can they do their job? Yes, they can...not an easy job, and sometimes a project don't make it or has some delays, but what the hack, that's how it works in the ICT!
GREAT job! or NOT?............What about the customers? Do we solve their problems?
Let's look at the Application Lifecycle Management [ALM] level
Try to answer this question: If the same bad requirements are sent to 10 different projects with the same assignment to make the needed Information System. What is the change that the projects will deliver an Information System that solves the problems of the customer?..............I think that, of course depending on the amount of communication with the customer during the projects, the changes are not very great, maybe some projects will, but most of them will need more than one release....
And that's NOT a GREAT job!
I know....we testers can't solve this problem.... but what, if we stop accepting Verbal Diarrhea as a test base....
What will happen if testers refuse to make test cases from bad requirements?

Or even....what happens if testers create, as a first step of the activity 'test case specification', for instance during the testability review, formal models like process flows or activity diagrams?
Problems like interpretations and/or assumptions rise instantly, and if these problems in the requirements can be solved before the development team start building the software, it would differ a lot!!
In this 'First Model then Test'(FMTT) approach , we can use the following set of models:
- Process Flows and/or Activity Diagrams for sequential processes/activities,
- CRUD matrices for database manipulations,
- Pseudo Code for business rules and validations,
- State Transition Diagrams for state dependent processes/activities.
Disadvantages of FMTT:
- Investment comes before profit: the testability review will take longer,
- You need to know more about models and modeling,
- It's different as we usually do,
- Performing the tests is less complex, less creative.
Advantages of 'First Model then Test' (FMTT):
- Finding Bugs As Early As Possible,
- The development and test process is less human dependant,
- Less interpretations and assumptions are needed during the building and testing,
- Less bugs to find (some will consider this as a disadvantage....),
- It's fun to collaborate with the other parties in Application Lifecycle Management [ALM],
- We testers help developers create higher quality systems.
Afraid to be bored by less complexity?
Try to make the next step: Model Based Development, Testing and/or Estimation!
I've already proved that generating test cases from models is possible (see previous articles on that subject).
Rob Kuijt




 ( 2.8 / 1160 )
( 2.8 / 1160 )

 Application Lifecycle Management [ALM] should ensure that an organization experiences an improved "business as usual" in the event of the implementation of new and/or changed functionality. Other (older) industries can give assurance, so the ICT industry should follow (soon?). This article will, I hope, give some next steps towards adulthood, by giving [ALM] directions how to prevent costly or even lethal disasters caused by bugs.
Application Lifecycle Management [ALM] should ensure that an organization experiences an improved "business as usual" in the event of the implementation of new and/or changed functionality. Other (older) industries can give assurance, so the ICT industry should follow (soon?). This article will, I hope, give some next steps towards adulthood, by giving [ALM] directions how to prevent costly or even lethal disasters caused by bugs.  Business Continuity has for [ALM] two viewpoints:
Business Continuity has for [ALM] two viewpoints: How to prevent a major disruption caused by the implementation of a new or changed application?
How to prevent a major disruption caused by the implementation of a new or changed application?  Pillar 1: Finding Bugs AEAP (As Early As Possibly)
Pillar 1: Finding Bugs AEAP (As Early As Possibly)  Testing Requirements
Testing Requirements Collaboration is a critical success factor in preventing a major disruption caused by the implementation of a new or changed application! All parties within [ALM] have to work together in creating good test coverage from the early until the last phases of the projects. I am sure that only when the Quality Levels, Learning Cycles and Metrics are in place, a good Business Continuity risk advice can be given to ensure that an organization experiences an improved "business as usual" in the event of the implementation of new and/or changed functionality.
Collaboration is a critical success factor in preventing a major disruption caused by the implementation of a new or changed application! All parties within [ALM] have to work together in creating good test coverage from the early until the last phases of the projects. I am sure that only when the Quality Levels, Learning Cycles and Metrics are in place, a good Business Continuity risk advice can be given to ensure that an organization experiences an improved "business as usual" in the event of the implementation of new and/or changed functionality. 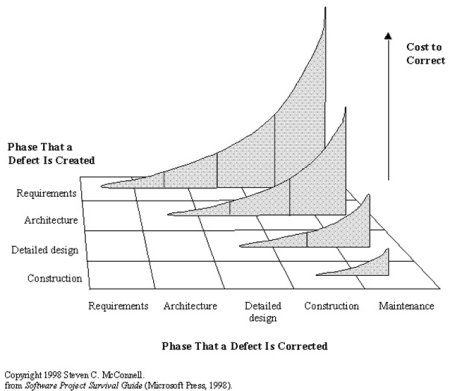



 Calendar
Calendar





